本文介绍WordPress 网站如何有效防止爬虫消耗资源,通过此方法可以有效避免部分垃圾爬虫,或者不遵守 robots 文件规则的爬虫,一直对网站进行暴力爬取,消耗网站内存资源的情况。
起因是我的客户站点一直内存告警,并且网站掉线,经过对日志的分析,看到一段时间内很多爬虫记录,并一直在爬取后台插件,主机以及 include 和缓存目录,导致网站内存压力非常大。
于是让 AI 帮我写了一些有效防止爬虫暴力爬取的代码,可以有效阻止爬虫去爬取后台目录。
1. robots.txt 方法
这个方法不是特别推荐,因为有部分爬虫它不遵守 Robots 文件规则。
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Disallow: /wp-includes/
Disallow: /wp-content/plugins/
Disallow: /wp-content/themes/
Disallow: /wp-content/cache/
Disallow: /wp-json/
Disallow: /xmlrpc.php
Disallow: /readme.html
Disallow: /license.txt
# 如果有自定义后台路径
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /backend/
Disallow: /login20251101/
# 特别强调缓存目录
Disallow: /cache/
Disallow: /wp-content/cache/min/
Disallow: /wp-content/cache/background-css/2. Nginx 配置方法
如果你可以访问 Nginx 配置文件可以使用这个方法,从 Nginx 中屏蔽和保护文件访问。
# 阻止爬虫访问敏感目录(包含缓存目录)
location ~* ^/(wp-admin|wp-includes|wp-content/plugins|wp-content/themes|wp-content/cache|admin|backend) {
# 方法A: 直接拒绝所有访问(最安全)
deny all;
return 404;
# 方法B: 仅阻止爬虫(推荐)
# if ($http_user_agent ~* (bot|crawl|spider|slurp|bingbot|googlebot|yahoo|baiduspider|yandex|sogou|duckduckbot)) {
# return 444;
# }
}
# 特别保护缓存目录
location ~* ^/wp-content/cache/ {
# 阻止所有爬虫
if ($http_user_agent ~* (bot|crawl|spider|slurp)) {
return 444;
}
# 允许正常用户访问,但阻止目录列表
location ~* /wp-content/cache/$ {
deny all;
return 404;
}
}
# 阻止特定的缓存子目录
location ~* ^/wp-content/cache/(min|background-css|wp-rocket)/ {
if ($http_user_agent ~* (bot|crawl|spider)) {
return 444;
}
}3. .htaccess 方法(Apache )
这是写在.htaccess文件中的防范,针对 Apache 服务。
# 阻止爬虫访问后台和缓存目录
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
# 阻止爬虫访问wp-admin
RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} (bot|crawl|spider|slurp|bingbot|googlebot|yahoo|baiduspider) [NC]
RewriteRule ^(wp-admin|wp-includes)/ - [F]
# 阻止爬虫访问缓存目录
RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} (bot|crawl|spider) [NC]
RewriteRule ^wp-content/cache/ - [F]
# 阻止访问特定的缓存子目录
RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} (bot|crawl|spider) [NC]
RewriteRule ^wp-content/cache/(min|background-css)/ - [F]
# 阻止插件和主题目录
RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} (bot|crawl|spider) [NC]
RewriteRule ^wp-content/(plugins|themes)/ - [F]
</IfModule>
# 使用FilesMatch直接阻止
<FilesMatch "\.(html|css|js)$">
SetEnvIfNoCase User-Agent ".*(bot|crawl|spider).*" BlockBot
Order Allow,Deny
Allow from all
Deny from env=BlockBot
</FilesMatch>4. WordPress 专用方法(PHP 代码)
这个可以直接加在网站的 Function.php 文件中的代码,阻止爬虫爬取后台文件的,你可以使用 CodeSnippet 这样的插件添加,适合大多数场景,我自己也用的这方法,只要有后台管理权限就可以实现。
// 阻止爬虫访问后台和缓存目录
function block_bots_from_sensitive_dirs() {
$current_path = $_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'] ?? '';
$user_agent = $_SERVER['HTTP_USER_AGENT'] ?? '';
$sensitive_paths = array(
'/wp-admin/',
'/wp-includes/',
'/wp-content/plugins/',
'/wp-content/themes/',
'/wp-content/cache/',
'/wp-json/'
);
$bots = array('bot', 'crawl', 'spider', 'slurp', 'bingbot', 'googlebot');
foreach ($sensitive_paths as $path) {
if (strpos($current_path, $path) !== false) {
foreach ($bots as $bot) {
if (stripos($user_agent, $bot) !== false) {
status_header(403);
die('Access Denied');
}
}
}
}
}
add_action('init', 'block_bots_from_sensitive_dirs');
// 在robots.txt中动态添加规则
function enhanced_robots_txt($output, $public) {
$output .= "# 保护敏感目录\n";
$output .= "Disallow: /wp-admin/\n";
$output .= "Disallow: /wp-includes/\n";
$output .= "Disallow: /wp-content/plugins/\n";
$output .= "Disallow: /wp-content/themes/\n";
$output .= "Disallow: /wp-content/cache/\n";
$output .= "Disallow: /wp-json/\n";
$output .= "Disallow: /xmlrpc.php\n\n";
$output .= "# 缓存子目录\n";
$output .= "Disallow: /wp-content/cache/min/\n";
$output .= "Disallow: /wp-content/cache/background-css/\n";
return $output;
}
add_filter('robots_txt', 'enhanced_robots_txt', 10, 2);5. 综合解决方案(Nginx 配置文件推荐生产环境使用)
这个代码写的比较全面细致,但是需要在 Nginx 配置文件中修改。
# Nginx 综合防护配置
server {
# 基础敏感目录防护
location ~* ^/(wp-admin|wp-includes|wp-content/plugins|wp-content/themes|admin) {
deny all;
return 404;
}
# 缓存目录特殊处理 - 允许访问文件但阻止目录遍历和爬虫
location ~* ^/wp-content/cache/ {
# 阻止目录列表
autoindex off;
# 阻止爬虫访问
if ($http_user_agent ~* (bot|crawl|spider|slurp|bingbot|googlebot)) {
return 444;
}
# 允许正常用户访问缓存文件
# 这里不设置deny all,因为正常用户需要访问缓存资源
}
# 特定的缓存子目录可以完全封锁
location ~* ^/wp-content/cache/(min|background-css)/ {
# 完全阻止访问这些生成目录
deny all;
return 404;
}
# 阻止登录页面被爬虫访问
location ~* ^/(wp-login|login20251101) {
if ($http_user_agent ~* (bot|crawl|spider)) {
return 444;
}
}
# 阻止敏感文件访问
location ~* \.(sql|bak|inc|txt|log|env|git)$ {
deny all;
return 404;
}
}缓存目录特别说明
对于 /wp-content/cache/ 目录需要特别注意:
允许访问的情况:
- ✅ 正常用户访问缓存的CSS/JS文件
- ✅ 网站正常加载需要缓存资源
需要阻止的情况:
- ❌ 爬虫扫描缓存目录结构
- ❌ 访问缓存目录列表
- ❌ 爬虫分析缓存文件内容
验证配置
配置成功后,您将在日志中看到:
- 爬虫访问缓存目录 → 返回444/403状态码
- 正常用户访问缓存文件 → 正常200状态码
- 爬虫访问其他敏感目录 → 返回404状态码
这样既保护了缓存目录不被爬虫扫描,又不影响网站正常功能。
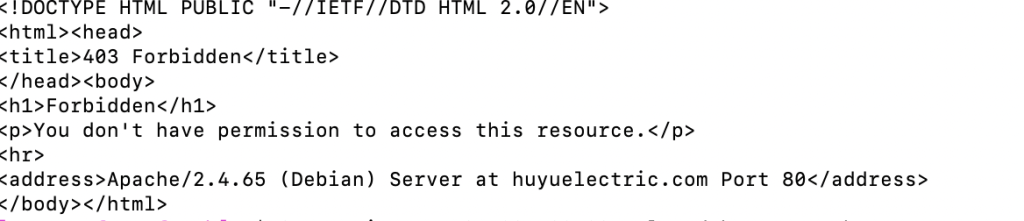
使用 Shell 执行测试
# 测试爬虫访问缓存目录(应该被阻止)
curl -A "Googlebot" https://yoursite.com/wp-content/cache/
curl -A "Bingbot" https://yoursite.com/wp-content/cache/min/
# 测试正常用户访问(应该允许)
curl -A "Chrome" https://yoursite.com/wp-content/cache/some-file.css如果模拟爬虫访问,返回结果是 403 fobidden,代表配置成功!